Prof. Dr. Thomas Wiegand - Magnetic Resonance of Complex Materials and Catalysts
- Prof. Dr. Thomas Wiegand
- Research Group Leader
- Magnetic Resonance of Complex Materials and Catalysts
- +49 (0)241 80 26420
- thomas.wiegand(at)cec.mpg.de
Vita
| Diploma | Chemistry, Westfälische-Wilhelms Universität Münster, Germany (2010) |
| PhD Thesis | Prof. Hellmut Eckert, Westfälische-Wilhelms Universität Münster, Germany/ Institute of Physical Chemistry (2010-2013) |
| PostDoc | Prof. Hellmut Eckert, Westfälische-Wilhelms Universität Münster, Germany/ Institute of Physical Chemistry (2013-2014) |
| PostDoc | Prof. Beat H. Meier, ETH Zürich, Switzerland/ Laboratory of Physical Chemistry (2014-2020) |
| Habilitation | ETH Zürich, Switzerland/ Laboratory of Physical Chemistry (2019) |
| Venia Legendi | ETH Zürich, Switzerland/ Laboratory of Physical Chemistry (2020) |
| Oberassistent/Privatdozent | ETH Zürich, Switzerland/ Laboratory of Physical Chemistry (2020-2021) |
| Research Group Leader | “Magnetic resonance of complex materials and catalysts”, MPI CEC (since 2021) |
| W2-Heisenberg-Professor | “Magnetic resonance of complex materials and catalysts”, MPI CEC/RWTH Aachen (since 2021) |
Group Members
Publications
Full publications list | ORCID | Researcher ID / Publons
- Silva, I. d. A., Bartalucci, E., Bolm, C., Wiegand, T. (2023). Opportunities and Challenges in Applying Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy in Organic Mechanochemistry. ADVANCED MATERIALS. doi:10.1002/adma.202304092.
- Sodreau, A., Zahedi, H. G., Dervisoglu, R., Kang, L., Menten, J., Zenner, J., Terefenko, N., DeBeer, S., Wiegand, T., Bordet, A., Leitner, W. (2023). A Simple and Versatile Approach for the Low-Temperature Synthesis of Transition Metal Phosphide Nanoparticles from Metal Chloride Complexes and P(SiMe3)3. ADVANCED MATERIALS. 2306621 (1-9) doi:10.1002/adma.202306621.
- Rout, S. K., Cadalbert, R., Schröder, N., Wang, J., Zehnder, J., Gampp, O., Wiegand, T., Güntert, P., Klingler, D., Kreutz, C., Knörlein, A., Hall, J., Greenwald, J., Riek, R. (2023). An Analysis of Nucleotide-Amyloid Interactions Reveals Selective Binding to Codon-Sized RNA. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 145(40), 21915-21924. doi:10.1021/jacs.3c06287.
- Callon, M., Luder, D., Malär, A. A., Wiegand, T., Rimal, V., Lecoq, L., Böckmann, A., Samoson, A., Meier, B. H. (2023). High and fast: NMR protein-proton side-chain assignments at 160 kHz and 1.2 GHz. CHEMICAL SCIENCE, 14(39), 10824-10834. doi:10.1039/d3sc03539e.
- Zhang, Y., El Sayed, S., Kang, L., Sanger, M., Wiegand, T., Jessop, P. G., DeBeer, S., Bordet, A., Leitner, W. (2023). Adaptive Catalysts for the Selective Hydrogenation of Bicyclic Heteroaromatics using Ruthenium Nanoparticles on a CO2-Responsive Support. Angewandte Chemie, International Edition in English, (XX): e202311427, pp. x-xx. doi:10.1002/anie.202311427.
- Pfister, S., Rabl, J., Wiegand, T., Mattei, S., Malaer, A. A., Lecoq, L., Seitz, S., Bartenschlager, R., Boeckmann, A., Nassal, M., Boehringer, D., Meier, B. H. (2023). Structural conservation of HBV-like capsid proteins over hundreds of millions of years despite the shift from non-enveloped to enveloped life-style. Nature Communications, (14): 1574, pp. 1-15. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-37068-w.
- Lipinski, W. P. P., Zehnder, J., Abbas, M., Güntert, P., Spruijt, E., Wiegand, T. (2023). Fibrils Emerging from Droplets: Molecular Guiding Principles behind Phase Transitions of a Short Peptide-Based Condensate Studied by Solid-State NMR. Chemistry – A European Journal,(29) e202301159, pp. 1-11. doi:10.1002/chem.202301159.
- Bartalucci, E., Malär, A. A. A., Mehnert, A., Büning, J. B. K. B., Günzel, L., Icker, M., Börner, M., Wiebeler, C., Meier, B. H. H., Grimme, S., Kersting, B., Wiegand, T. (2023). Probing a Hydrogen-pi Interaction Involving a Trapped Water Molecule in the Solid State. Angewandte Chemie, International Edition in English, (62), 1-10,e2022177 . doi:10.1002/anie.202217725.
- Bartalucci, E., Luder, D. J., Terefenko, N., Malär, A. A., Bolm, C., Ernst, M., Wiegand, T. (2023). The effect of methyl group rotation on H-1-H-1 solid-state NMR spin-diffusion spectra. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, (25), 19501-19511. doi:10.1039/d3cp02323k.
- Bartalucci, E., Schumacher, C., Hendrickx, L., Puccetti, F., d'Anciaes Almeida Silva, I., Dervisoglu, R., Puttreddy, R., Bolm, C., Wiegand, T. (2023). Disentangling the Effect of Pressure and Mixing on a Mechanochemical Bromination Reaction by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Chemistry – A European Journal, e202203466, pp. 1-12. doi:10.1002/chem.202203466.
- Lacabanne, D., Wiegand, T., Di Cesare, M., Orelle, C., Ernst, M., Jault, J.-M., Meier, B. H., Boeckmann, A. (2022). Solid-State NMR Reveals Asymmetric ATP Hydrolysis in the Multidrug ABC Transporter BmrA. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 144(27), 12431-12442. doi:10.1021/jacs.2c04287.
- Malär, A. A., Sun, Q., Zehnder, J., Kehr, G., Erker, G., Wiegand, T. (2022). Proton-phosphorous connectivities revealed by high-resolution proton-detected solid-state NMR. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 24(13), 7768-7778. doi:10.1039/d2cp00616b.
- Zehnder, J.; Cadalbert, R.; Yulikov, M.; Künze, G.; Wiegand, T. (2021) Paramagnetic spin labeling of a bacterial DnaB helicase for solid-state NMR, J. Magn. Reson., 332, 107075, DOI:10.1016/j.jmr.2021.107075
- Malär, A.A., Wili, N., Völker, L.A., Kozlova, M.I., Cadalbert, R., Däpp, A., Weber, M. E., Zehnder, J. , Jeschke, G. , Eckert, H. , Böckmann, A. , Klose, D. , Mulkidjanian, A.Y., Meier, B.H. , Wiegand, T. (2021) Spectroscopic glimpses of the transition state of ATP hydrolysis trapped in a bacterial DnaB helicase, Nat. Commun., 12, 5293 doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25599-z
- Chávez, M., Wiegand, T., Malär, A. A., Meier, B. H. , Ernst, M.(2021) Residual Linewidth in Magic-Angle Spinning Proton Solid-State NMR, Magnetic Resonance, 2, 499-509. doi.org/10.5194/mr-2-499-2021
- Callon, M., Malär, A.A., Pfister, S., Rimal, V., Weber, M. E., Wiegand, T., Zehnder, J., Chavez, M., Deb, R., Däpp, A., Cadalbert, R., Fogeron, M.-L., Zyla, D., Hunkeler, A., Lecoq, L., Torosyan, A., Wang, S., Jonas, S., Glockshuber, R., Ernst, M., Böckmann, A., Meier, B.H. (2021) Biomolecular solid-state NMR spectroscopy at 1200 MHz: the gain in resolution, J. Biomol. NMR, 75, 255-272. doi.org/10.1007/s10858-021-00373-x
- Malär, A.A,, Völker, L.A.,Cadalbert, R., Ernst, M., Böckmann,A, Meier,B.H., Wiegand,T. (2021) Temperature-dependent solid-state NMR proton chemical-shift values and hydrogen bonding, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2021, 125, 6222-6230 doi/pdf/10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c04061
- Zehnder, J., Cadalbert, R., Terradot, L., Ernst, M., Böckmann, A., Güntert, P., Meier, B.H., Wiegand, T. (2021) Paramagnetic solid-state NMR to localize the metal-ion cofactor in an oligomeric DnaB helicase, Chemistry 27, 7745-7755 doi.org/10.1002/chem.202100462
- Lecoq, L., Wang, S., Dujardin, M., Zimmermann, P., Schuster, L., Fogeron, M.-L, Briday, M., Schledorn, M., Wiegand, T., Cole, A.L, Montserrat, R., Bressanelli, S., Meier, B.H., Nassal, M., Böckmann A. (2021) A pocket-factor-triggered conformational switch in the hepatitis B virus capsid, PNAS, 118, e2022464118. doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2022464118
- Kumari, P. , Gosh, D. , Vanas, A. ,. Fleischmann, Y, Wiegand, T. , Jeschke, G. , Riek, R. Eichmann, C.(2021) Structural Insights into α-Synuclein Monomer-Fibril Interactions, PNAS, 118, e2012171118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012171118
- Lacabanne, D.; Boudet, J.; Malär, A. A. ; Wu, P. ; Cadalbert, R. ; Salmon, L.; Allain, F. H.-T. ; Meier, B. H.; Wiegand, T. (2020) Protein side-chain-DNA contacts probed by fast magic-angle spinning NMR. J. Phys. Chem. B (124) 11089-11097 doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c08150
- Wiegand, T.; Malär, A. A.; Cadalbert, R.; Ernst, M.; Böckmann, A.; Meier, B.H. (2020) Asparagine and glutamine side-chains and ladders in HET-s(218-289) amyloid fibrils studied by fast magic-angle spinning NMR. Frontiers Mol. Biosc.(7) 582033 doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2020.582033
- Wiegand, T.; Lacabanne, D.; Torosyan, A.; Boudet, J.; Cadalbert, R.; Allain, F. H.-T. ; Meier, B. H.; Böckmann, A. (2020) Sedimentation yields long-term stable protein samples as shown by solid-state NMR. Frontiers Mol. Biosc. (7) 17 DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00017
- Wiegand, T.; Schledorn, M.; Malär, A. A. R. Cadalbert, R.; Däpp, A.; Terradot, L.; Meier, B. H.; Böckmann, A. (2020) Nucleotide binding modes in a motor protein revealed by 31P- and 1H-detected MAS solid-state NMR . ChemBioChem (21) 324-330 DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201900439
- Torosyan, A; , Wiegand.T ; Schledorn, M.; Klose, D.; Güntert, P.; Böckmann, A.; Meier, B. H. (2019) Including protons in solid-state NMR resonance assignment and secondary structure analysis: The example of RNA polymerase II subunits Rpo4/7. Frontiers Mol. Biosc. (6) 100. doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2019.00100
- Malär, A. A.; Smith-Penzel, S.; Camenisch, G.-M. ; Wiegand, T.; Samoson, A.; Böckmann, A.; Ernst, M.; Meier, B. H. (2019) Quantifying NMR Coherent Proton Linewidth in Proteins Under Fast MAS Conditions: A Second Moment Approach, PhysChemChemPhys (21) 18850-18865 doi: 10.1039/c9cp03414e
- Lacabanne, D.; Orelle, C.; Lecoq, L.; Kunert, B. ; Chuilon, C. ; Wiegand, T.; Ravaud, S.; Jault, J.-M. ; Meier, B. H.; Böckmann, A. (2019) Flexible-to-rigid transition is central for substrate transport in the ABC transporter BmrA from Bacillus subtilis, Commun. Biol. (2) 1-9 doi.org/10.1038/s42003-019-0390-x |
- Malär, A. A.; Dong, S.; Kehr, G.; Erker, G.; Meier, B. H.; Wiegand T. (2019) Characterization of H2-splitting products of Frustrated Lewis Pairs: Benefit of fast magic-angle spinning. ChemPhysChem, (20) 672-679 doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201900006
- Wiegand T. ; Cadalbert, R.; Lacabanne, D.; Timmins, J. ; Terradot, L. ; Böckmann, A.; Meier, B. H. (2019) The conformational changes coupling ATP hydrolysis and translocation in a bacterial DnaB helicase. Nat. Commun. (10) 31 doi:10.1038/s41467-018-07968-3
- Boudet, J.; Devillier, J.-C. ; Wiegand T.; Salmon, L.; Meier, B. H.; Lipps, G.; Allain, F. H.-T. (2019) A small helical bundle prepares primer synthesis by binding two ATP nucleotides that enhance sequence-specific recognition of the DNA template. Cell, (176) 154-166. doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.031
Magnetic Resonance of Complex Materials and Catalysts
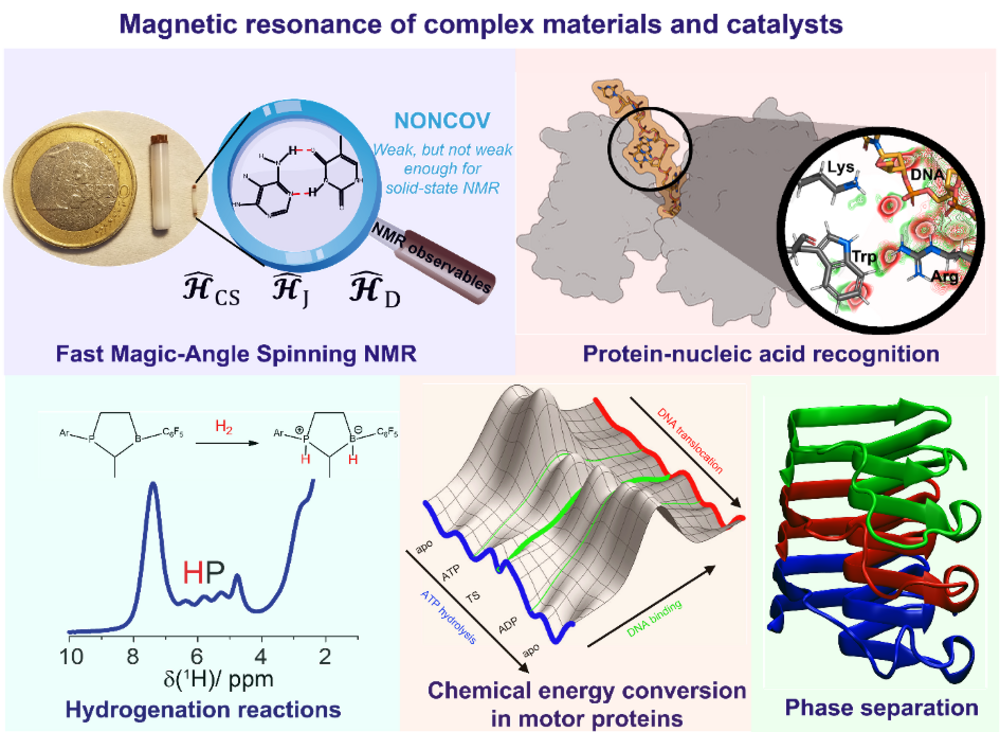
We use magnetic-resonance spectroscopy to study catalytic processes in biology and chemistry and the role of weak noncovalent interactions therein. In particular, we are employing and developing solid-state Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) approaches with which even non-crystalline systems, such as hydrogels, amorphous polymers, particles on solid surfaces, protein fibrils or large protein-nucleic acid complexes, can be studied. A focus of our research lies on the detection of protons, which often are at the heart of a molecular recognition event initiating chemical reactions or assembly processes. Until recently, however, their solid-state NMR spectra used to be uninformative due to lack of resolution. However, with the significant line-narrowing achieved with the advent of new fast magic-angle spinning (MAS) techniques (MAS frequencies larger than 100 kHz) the protons engaged in various types of noncovalent interactions (hydrogen bondings, π-π- or hydrophobic interactions etc.) can be resolved and identified. We interpret our experimental results in feedback with quantum-chemical calculations on how NMR observables are influenced by noncovalent interactions.
Our vision is to develop unified concepts in catalysis bridging the gap between biology and chemistry. Our strategies to study mechanisms of hydrogenation reactions include both, fast MAS and Para-hydrogen Induced Polarization (PHIP) experiments. Interesting model systems are, for instance, Frustrated Lewis Pairs that can activate and bind small molecules such as di-hydrogen. In the biomolecular context, we investigate cellular organization by phase separation processes in proteins related to neurodegenerative diseases (e.g. RNA-binding proteins). Liquid-liquid phase separation is an intensively debated concept these days allowing cells to spatially and temporarily regulate biological reactions in subcompartments, such as membrane-less organelles. We are developing the solid-state NMR and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) toolboxes to explore the liquid-to-solid transition of proteins and to probe the weak noncovalent interactions driving such processes. Another central research theme in our lab is the mechanism of chemical energy conversion in proteins, for instance in ATP-fuelled motor proteins involved in DNA replication. Here we investigate the binding of nucleic acids to proteins, allowing us to develop models for ATP-hydrolysis and its correlation with protein functionality. The newly established techniques will also allow us to investigate the role of RNA in phase separation events.
We are always looking for enthusiastic semester, bachelor, master or doctoral students and are curious to get to know you.